Choosing sustainable packaging is great—but which option actually saves you money during shipping?
Comparing PLA and PET bottles in logistics reveals clear differences in weight, volume efficiency, and durability that directly affect your cost per unit delivered.
At PauPack, we serve global beauty and wellness brands who care about sustainability and supply chain savings. Here's how PLA and PET bottles stack up in the real world of freight and fulfillment.
What Are the Key Material Differences Between PLA and PET Bottles?
Sustainability starts with the source, but performance ends with how your bottles travel.
PLA is a plant-based, biodegradable material, while PET is petroleum-based and known for its clarity and strength—each with different logistic implications.
Material Overview
| Feature | PLA | PET |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Corn starch / sugarcane | Petroleum |
| Biodegradability | Compostable in industrial setup | Fully recyclable |
| Transparency | Slightly opaque | Highly transparent |
| Thermal resistance | Lower (warps over 45°C) | High (up to 70°C or more) |
In essence, PLA is ideal for brands pushing eco-packaging and low-impact branding. PET remains the dominant choice for performance, clarity, and established recycling logistics.
PauPack supports both material types across our essential oil, lotion, and spray bottle collections—allowing you to choose based on your priorities and freight realities.
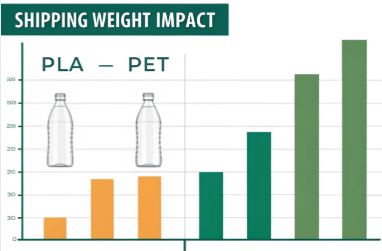
How Do Weight and Density Affect Shipping Costs?
When you're shipping 10,000 bottles, grams matter.
PLA bottles tend to be lighter than PET, reducing shipping weight—but PET’s better strength-to-weight ratio may result in fewer damaged goods.
Weight Comparison
| Bottle Size | PLA Bottle Weight | PET Bottle Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 100ml | ~9g | ~12g |
| 250ml | ~15g | ~20g |
| 500ml | ~25g | ~30g |
On a pallet level:
-
1,000 PLA bottles @ 100ml = ~9kg
-
1,000 PET bottles @ 100ml = ~12kg
Assuming $2/kg international air freight, that’s a savings of $6 per 1,000 bottles. Over 100,000 bottles, you’re saving $600—small, but significant when margins are tight.
At PauPack, we run lightweighting simulations during packaging design, showing clients projected freight savings with PLA vs PET options.
Which Bottle Type Performs Better in Storage and Pallet Efficiency?
What good is saving on weight if you lose volume to inefficient stacking?
PET’s rigidity offers better structural integrity for high stacking, while PLA bottles may require more protective spacing due to fragility and warping risk.
Pallet Utilization
| Bottle Type | Bottles per Pallet | Layer Stability | Compression Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | ~1,500–2,000 | High | Excellent |
| PLA | ~1,200–1,800 | Medium | Lower (needs liners) |
PLA bottles can deform slightly under load, especially if exposed to heat. This can reduce the effective pallet count and increase your storage cost per bottle.
At PauPack, we use reinforced cartons and optimized dividers for PLA bottles, minimizing deformation risk during sea and warehouse storage.
What Role Does Breakage and Temperature Resistance Play in Transit?
Shipping isn't just about distance—it's about survival.
PET bottles are more resistant to impact and temperature shifts, while PLA bottles require more protective packaging, increasing carton size and packing material use.
In-Transit Durability
-
PET Bottles: Withstand rough handling, flex under pressure, suitable for air, sea, and express freight.
-
PLA Bottles: Can warp under high heat (above 45°C), more brittle in cold (below 10°C), and require cushioning.
Environmental Risk Zones
| Risk Factor | Impact on PLA | Impact on PET |
|---|---|---|
| Summer sea freight | High (warping) | Low |
| Air cargo pressure | Medium (deform) | Low |
| Freezing temps | High (crack risk) | Low |
If your distribution includes long-haul or high-temp regions (like Australia, South America), PET remains a safer choice unless extra packaging costs are acceptable.
PauPack offers multilayer PLA bottles with improved heat resistance, suitable for indoor retail and last-mile delivery—but we still recommend PET for high-risk transit routes.
What’s the Final Verdict on Cost-Effective Logistics?
Sustainability is great—but so is keeping your margins intact.
PLA bottles save weight, making air freight slightly cheaper, but PET bottles often win overall due to superior stacking, fewer breakages, and better pallet density.
Summary Comparison
| Factor | PLA | PET |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Savings | ✅ | ❌ |
| Pallet Efficiency | ❌ | ✅ |
| Transit Durability | ❌ | ✅ |
| Eco Brand Appeal | ✅ | ✅ (Recyclable claim) |
| Cost per Bottle Shipped | Moderate Savings | Consistent Efficiency |
At PauPack, we help clients run cost simulations across shipping methods, climates, and storage setups. Whether you prioritize carbon impact or cost savings, our tailored packaging strategy ensures your bottles ship smart and sell better.
Why Logistics Costs Are Crucial in Packaging Material Decisions
You may love a sustainable material—but if it doubles your shipping cost, that love fades fast.
For high-volume B2B orders, even a 5% difference in freight efficiency can add up to thousands in annual costs—making logistics a core part of material strategy.
The Hidden Impact of Freight on COGS
When sourcing 50,000+ bottles at a time:
-
Freight weight affects air and express shipments
-
Cube utilization affects sea and warehouse cost
-
Damage rate affects loss and re-shipments
| Impact Factor | Adds Cost? | Typical Range (Per 10k bottles) |
|---|---|---|
| Overweight pallet | Yes | $100–$300 |
| Poor stacking | Yes | +1 extra pallet |
| Breakage in transit | Yes | 2–8% loss rate |
We often advise clients during their packaging planning to simulate freight with actual carton specs—not just unit cost—especially when scaling DTC logistics.
How Does Bottle Design Affect Freight Volume and Stackability?
Not all 100ml bottles ship equally. Shape = cost.
Tall-neck PLA bottles may deform and reduce stack height, while short, squat PET bottles allow for tighter packing and higher pallet utilization.
Freight Geometry Matters
A typical 100ml bottle can be:
-
Tall and thin (15cm high) → higher wasted headspace
-
Short and wide (10cm high) → better carton fill rate
| Bottle Shape | Max Carton Count | Pallets per Container | Stack Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tall PLA Cylinder | 360 | 15 | Medium |
| PET Round Boston | 480 | 18 | High |
| PLA Oval (Flats) | 400 | 16 | Low |
We at PauPack offer bottle re-engineering services for clients looking to balance aesthetics with freight efficiency, reducing cube waste by up to 20%.
What Are the Real-world Shipping Costs of PLA vs PET?
Let’s get to the numbers: which one hits your freight budget harder?
PLA bottles reduce weight-based fees slightly, but PET wins overall in container fill rates, less padding needs, and fewer repacks after damage.
Freight Simulation: China to USA, 100,000 Bottles (100ml)
| Cost Factor | PLA Estimate | PET Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| Weight (air cargo) | $1,800 | $2,200 |
| Sea freight pallets | 80 pallets | 68 pallets |
| Pallet handling fee | $1,600 | $1,360 |
| Loss from damage (2%) | $750 | $250 |
Total Cost (Air): PLA wins
Total Cost (Sea + Warehouse): PET wins
Conclusion: If you're doing short-haul air or small batch e-commerce, PLA offers modest gains. For global fulfillment and FCL containers, PET has the edge.
PauPack provides clients with a logistics cost calculator that inputs SKUs, destination, and transport method to project the most cost-efficient packaging mix.
How Do Temperature and Climate Influence Bottle Choice?
Your logistics route could make or break your PLA plan.
PLA softens at around 45°C, making it vulnerable in containers crossing hot climates. PET, with a higher thermal threshold, is far more shipping-resilient.
Risk Areas for PLA
-
Sea Freight via Tropics (Panama, Singapore): High heat inside containers
-
Desert Last-Mile (Southwest U.S., Middle East): Truck heat reaches 60°C
-
Cold-Chain Distribution: PLA gets brittle under 10°C
| Scenario | PLA Risk | PET Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Summer Ocean Freight | High | Low |
| Winter Air Cargo | Medium | Low |
| E-commerce Warehouse | Low | Low |
To mitigate this, PauPack offers PLA bottles with upgraded heat-resistant blends and insulated shipper boxes, though we still recommend PET for international fulfillment.
Can Sustainable Packaging Still Be Logistically Efficient?
Yes—but only if you plan both design and shipping together.
Sustainability and savings can align when brands co-optimize material, shape, closure, and carton layout—not just the bottle resin.
Optimization Strategies
-
Switch to squat PLA bottle design to save vertical space
-
Bundle closures separately to reduce internal pressure risk
-
Use partitioned cartons to minimize movement in transit
-
Choose hybrid bottles (rPET/PLA blends) for durability
At PauPack, we help clients design custom PLA packaging that ships as efficiently as PET—achieving up to 15% reduction in shipping cost while maintaining compostable claims.

Conclusion
In logistics, PLA is lighter—but PET is stronger. Choose based on your shipping route, volume, and damage tolerance. When optimized right, both can save you money—and save the planet.